T1W, T1 mapping and T1 Contrast Agent Imaging
T1 weighted image (T1W or "spin-lattice" relaxation time) is one of the basic image contrasts in MRI. A T1W relies upon the longitudinal relaxation of a tissue's net magnetization vector. T1W tends to have short TE and TR times. Fat appears bright on a T1W image, water has low signal and appears dark. T1W provides the best contrast for paramagnetic contrast agents (e.g. gadolinium-containing compounds).
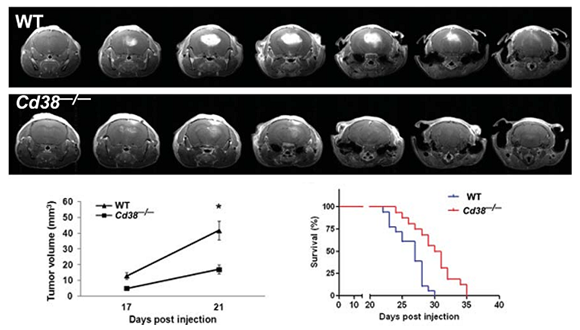
Levy A et.al (2012)
Publication from our center:
Aizman E, Mor A, Chapman J, Assaf Y, Kloog Y. 2010. The combined treatment of Copaxone and Salirasib attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Neuroimmunol 229:192-203.
Amram N, Hacohen-Kleiman G, Sragovich S, Malishkevich A, Katz J, Touloumi O, Lagoudaki R, Grigoriadis NC, Giladi E, Yeheskel A, Pasmanik-Chor M, Jouroukhin Y, Gozes I. 2016. Mol Psychiatry. Jan 19.
De Santis S, Barazany D, Jones DK, Assaf Y. 2015.Resolving relaxometry and diffusion properties within the same voxel in the presence of crossing fibres by combining inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted acquisitions.Magn Reson Med.
Elron-Gross I, Glucksam Y, Biton IE, Margalit R. 2009. A novel Diclofenac-carrier for local treatment of osteoarthritis applying live-animal MRI. J Control Release 135:65-70.
Izraely S, Sagi-Assif O, Klein A, Meshel T, Tsarfaty G, et al. (Witz I) 2011. The metastatic microenvironment: Brain-residing melanoma metastasis and dormant micrometastasis. Int J Cancer : 131(1071-1082).
Jouroukhin Y, Ostritsky R, Assaf Y, Pelled G, Giladi E, Gozes I. 2013 NAP davunetide) modifies disease progression in a mouse model of severe neurodegeneration: protection against impairments in axonal transport. Neurobiol Dis. 56:79-94.
Levy H, Assaf Y, Frenkel D. 2010. Characterization of brain lesions in a mouse model of progressive multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol 226:148-58.
Levy Barazany H, Barazany D, Puckett L, Blanga-Kanfi S, Borenstein-Auerbach N, Yang K, Peron JP, Weiner HL, Frenkel D. 2014. Brain MRI of nasal MOG therapeutic effect in relapsing-progressive EAE. Exp Neurol 255:63-70.
Levy A, Blacher E, Vaknine H, Lund FE, Stein R, Mayo L. 2012. CD38 deficiency in the tumor microenvironment attenuates glioma progression and modulates features of tumor-associated microglia/macrophages. Neuro Oncol. 14(8):1037-49.
Lifshitz V, Weiss R, Benromano T, Kfir E, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, et al. 2012. Immunotherapy of cerebrovascular amyloidosis in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 33:432 e1- e13.
Turjeman K, Bavli Y, Kizelsztein P, Schilt Y, Allon N, Katzir TB, Sasson E, Raviv U, Ovadia H, Barenholz Y. 2015. Nano-Drugs Based on Nano Sterically Stabilized Liposomes for the Treatment of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0130442.
Inversion recovery MRI (IR-MRI)
Inversion recovery (IR) is condisered the gold standard method for measuring the longitudinal relaxation time, T1. The sequence starts with a 180°-pulse to invert the magnetization of water protons in the tissue, which then spontaneously relaxes back to its steady state. During the delay time τ that follows the spins are allowed to relax until a 90°-pulse creates observable, transverse magnetization and the FID is acquired. The magnitude and sign of the peaks in the spectrum depend on the longitudinal relaxation rate of each spin. If τ is systematically varied, the peak intensity as a function of τ is proportional to the z-magnetization just before the second pulse. The T1 times can be calculated by fitting the curve. FLAIR, is a specific case of IR-MRI with nulled signal of CSF fluid, arises mainly from the brain ventricles.
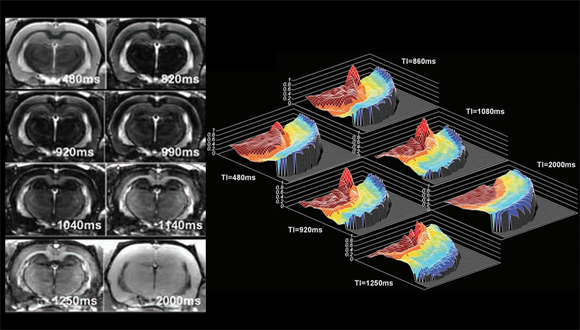
Barazany D et.al (2011)
Publication from our center:
Barazany D, Assaf Y. 2011. Visualization of Cortical Lamination Patterns with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cereb Cortex Oct 8.
T2W and T2 mapping
T2 weighted image (T2W) is one of the basic image contrasts in MRI. A T2W relies upon the transverse relaxation ("spin-spin" relaxation) of the net magnetisation vector. T2 weighting tends to require long TE and TR times. Each tissue has an inherent T2 value, fat: intermediate-bright, fluid: bright. T2, suited to imaging edema, T2 map showing gray matter abnormalities.
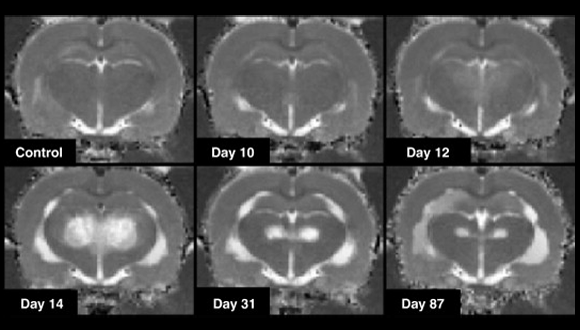
Dror V et.al (2009)
Publication from our center:
Aizman E, Mor A, Chapman J, Assaf Y, Kloog Y. 2010. The combined treatment of Copaxone and Salirasib attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Neuroimmunol 229:192-203.
Assaf Y, Galron R, Shapira I, Nitzan A, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, et al. 2008. MRI evidence of white matter damage in a mouse model of Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Exp Neurol 209:181-91.
Baranes K, Raz-Prag D, Nitzan A, Galron R, Ashery-Padan R, et al. 2009. Conditional inactivation of the NBS1 gene in the mouse central nervous system leads to neurodegeneration and disorganization of the visual system. Exp Neurol 218:24-32.
Dror V, Eliash S, Rehavi M, Assaf Y, Biton IE, Fattal-Valevski A. 2010. Neurodegeneration in thiamine deficient rats-A longitudinal MRI study. Brain Res 1308:176-84.
Klebanov O, Nitzan A, Raz D, Barzilai A, Solomon AS. 2009. Upregulation of Semaphorin 3A and the associated biochemical and cellular events in a rat model of retinal detachment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247:73-86.
Patrich E, Piontkewitz Y, Peretz A, Weiner I, Attali B .2016. Maturation- and sex-sensitive depression of hippocampal excitatory transmission in a rat schizophrenia model. Brain Behav Immun. 51:240-51.
Piontkewitz Y, Arad M, Weiner I. 2011a. Abnormal trajectories of neurodevelopment and behavior following in utero insult in the rat. Biol Psychiatry 70:842-51.
Piontkewitz Y, Arad M, Weiner I. 2011b. Risperidone administered during asymptomatic period of adolescence prevents the emergence of brain structural pathology and behavioral abnormalities in an animal model of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 37:1257-69.
Piontkewitz Y, Arad M, Weiner I. 2012. Tracing the development of psychosis and its prevention: what can be learned from animal models. Neuropharmacology 62:1273-89.
Piontkewitz Y, Assaf Y, Weiner I. 2009. Clozapine administration in adolescence prevents postpubertal emergence of brain structural pathology in an animal model of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 66:1038-46.
Robinson A, Kloog Y, Stein R, Assaf Y. 2010. Motor deficits and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-associated MRI impairments in a mouse model of NF1. NMR Biomed 23:1173-80.
Sadan O, Shemesh N, Barzilay R, Dadon-Nahum M, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, et al. 2012. Mesenchymal stem cells induced to secrete neurotrophic factors attenuate quinolinic acid toxicity: a potential therapy for Huntington's disease. Exp Neurol 234:417-27.
Sadan O, Shemesh N, Barzilay R, Dadon-Nahum M, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, et al. (Daniel Offen) 2012. Mesenchymal stem cells induced to secrete neurotrophic factors attenuate quinolinic acid toxicity: a potential therapy for Huntington's disease. Exp Neurol 234:417-27.
Shemesh N, Sadan O, Melamed E, Offen D, Cohen Y. 2010. Longitudinal MRI and MRSI characterization of the quinolinic acid rat model for excitotoxicity: peculiar apparent diffusion coefficients and recovery of N-acetyl aspartate levels. NMR Biomed 23:196-206.
Shrot S, Anaby D, Krivoy A, Makarovsky I, Rosman Y, et al. (Cohen Y) 2012. Early in vivo MR spectroscopy findings in organophosphate-induced brain damage-potential biomarkers for short-term survival. Magn Reson Med. 68(5):1390-8.
T2* Imaging
T2* contrast is mainly produced by a gradient echo (GRE) pulse sequence, which absent an extra refocusing pulse, thus the image is prone to susceptibility losses at air/tissue boundaries, and exhibit high sensitivity to venous blood.
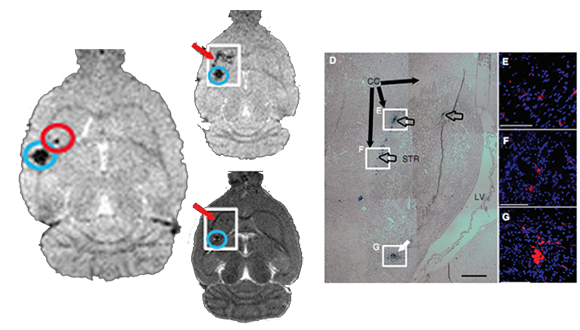
Sadan O et.al (2009)
Publication from our center:
Bar-Shir A, Avram L, Yariv-Shoushan S, Anaby D, Cohen S, Segev-Amzaleg N, Frenkel D, Sadan O, Offen D, Cohen Y.2014. Alginate-coated magnetic nanoparticles for noninvasive MRI of extracellular calcium. NMR Biomed 27(7):774-83
Sadan O, Bahat-Stromza M, Barhum Y, Levy YS, Pisnevsky A, et al. (Daniel Offen) 2009. Protective effects of neurotrophic factor-secreting cells in a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson disease. Stem Cells Dev 18:1179-90.
Sadan O, Shemesh N, Barzilay R, Bahat-Stromza M, Melamed E, et al. (Daniel Offen) 2008. Migration of neurotrophic factors-secreting mesenchymal stem cells toward a quinolinic acid lesion as viewed by magnetic resonance imaging. Stem Cells 26:2542-51.
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (1H-MRSI)
MRSI is used to measure the levels of different metabolites in body tissues. The MR signal produces a spectrum of resonances that correspond to different molecular arrangements of the isotope being "excited". This signature is used to diagnose certain metabolic disorders, especially those affecting the brain.
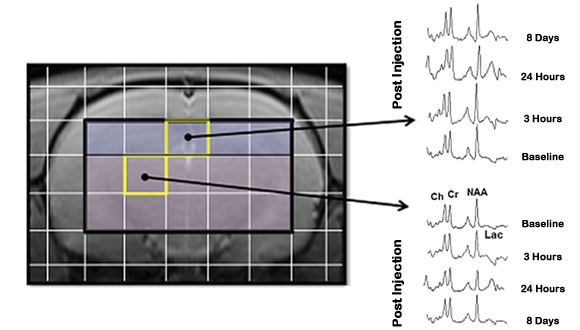
Shrot S et.al (2012)
Publication from our center:
Bar-Shir A, Shemesh N, Nossin-Manor R, Cohen Y. 2010. Late stimulation of the sphenopalatine-ganglion in ischemic rats: improvement in N-acetyl-aspartate levels and diffusion weighted imaging characteristics as seen by MR. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:1355-63.
Shrot S, Anaby D, Krivoy A, Makarovsky I, Rosman Y, et al. (Cohen Y) 2012. Early in vivo MR spectroscopy findings in organophosphate-induced brain damage-potential biomarkers for short-term survival. Magn Reson Med. 68(5):1390-8.
Diffusion Weighted and Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
In diffusion MRI the intensity of each voxel reflects the rate of water diffusion at its spatial location. As the mobility of water is highly dependent on its cellular environment, DWI may indicate an early pathologic change. (e.g., DWI is more sensitive to early changes after a stroke than T1W or T2W). Acquisition of DWI in six or more gradient directions, is sufficient to compute the diffusion tensor, which is based on a simpe model of the diffusion process, assuming homogeneity and linearity of the diffuion within each voxel. The diffusion anisotropy (FA) and the apparant diffusion coefficient (ADC) could be computed from the diffusion tensor. FA is mainly used to infer white matter connectivity (tractography) in the brain. The diffusion weighting is governed by the b-value.
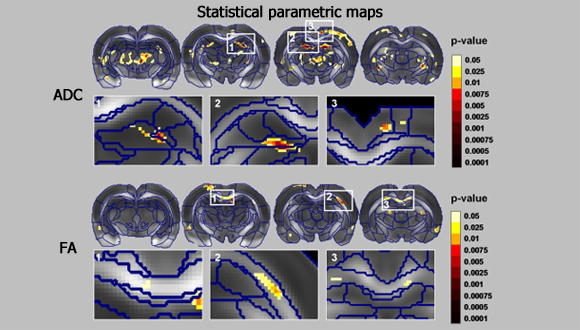
Blumenfeld-Katzir T et.al (2011)
Publication from our center:
Anaby D, Duncan ID, Smith CM, Cohen Y. 2013. White matter maturation in the brains of Long Evans shaker myelin mutant rats by ex-vivo QSI and DTI. NMR Biomed. 26(12):1879-86.
Amram N, Hacohen-Kleiman G, Sragovich S, Malishkevich A, Katz J, Touloumi O, Lagoudaki R, Grigoriadis NC, Giladi E, Yeheskel A, Pasmanik-Chor M, Jouroukhin Y, Gozes I. 2016. Mol Psychiatry. Jan 19.
Bar-Shir A, Duncan ID, Cohen Y. 2009. QSI and DTI of excised brains of the myelin-deficient rat. Neuroimage 48:109-16.
Bar-Shir A, Shemesh N, Nossin-Manor R, Cohen Y. 2010. Late stimulation of the sphenopalatine-ganglion in ischemic rats: improvement in N-acetyl-aspartate levels and diffusion weighted imaging characteristics as seen by MR. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:1355-63.
Blumenfeld-Katzir T, Pasternak O, Dagan M, Assaf Y. 2011. Diffusion MRI of structural brain plasticity induced by a learning and memory task. PLoS One 6:e20678
De Santis S, Barazany D, Jones DK, Assaf Y. 2015.Resolving relaxometry and diffusion properties within the same voxel in the presence of crossing fibres by combining inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted acquisitions.Magn Reson Med. [Epub ahead of print]. (IR-DTI for dtailes pg373)
Geva M, Cabilly Y, Assaf Y, Mindroul N, Marom L, et al. (Orna Elroy-Stein) 2010. A mouse model for eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B-leucodystrophy reveals abnormal development of brain white matter. Brain 133:2448-61
Hofstetter S, Tavor I, Tzur Moryosef S, Assaf Y. 2013. Short-term learning induces white matter plasticity in the fornix. J Neurosci. 33(31):12844-50.
Lamhot VB, Khatib N, Ginsberg Y, Anunu R, Richter-Levin G, Weiner Z, Ross MG, Divon MY, Hallak M, Beloosesky R. 2015. Magnesium sulfate prevents maternal inflammation-induced impairment of learning ability and memory in rat offspring.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213(6):851.e1-8.
Lax E, Friedman A, Croitoru O, Sudai E, Ben-Moshe H, Redlus L, Sasson E, Blumenfeld-Katzir T,Assaf Y, Yadid G. 2013. Neurodegeneration of lateral habenula efferent fibers after intermittent cocaine administration: implications for deep brain stimulation. Neuropharmacology. 75:246-54.
Levy H, Assaf Y, Frenkel D. 2010. Characterization of brain lesions in a mouse model of progressive multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol 226:148-58
Rubovitch V, Ten-Bosch M, Zohar O, Harrison CR, Tempel-Brami C, et al. 2011. A mouse model of blast-induced mild traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 232:280-9
Sagi Y, Tavor I, Hofstetter S, Tzur-Moryosef S, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, Assaf Y. 2012. Learning in the fast lane: new insights into neuroplasticity. Neuron 73:1195-203
Shemesh N, Sadan O, Melamed E, Offen D, Cohen Y. 2010. Longitudinal MRI and MRSI characterization of the quinolinic acid rat model for excitotoxicity: peculiar apparent diffusion coefficients and recovery of N-acetyl aspartate levels. NMR Biomed 23:196-206
Turjeman K, Bavli Y, Kizelsztein P, Schilt Y, Allon N, Katzir TB, Sasson E, Raviv U, Ovadia H, Barenholz Y. 2015. Nano-Drugs Based on Nano Sterically Stabilized Liposomes for the Treatment of Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0130442.
Zalsman G, Gutman A, Shbiro L, Rosenan R, Mann JJ, Weller A. 2015. Genetic vulnerability, timing of short-term stress and mood regulation: A rodent diffusion tensor imaging study.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 25(11):2075-85.
AxCaliber (multi Shell Diffusion MRI)
AxCaliber uses diffusion weighted MRI data along with a model of intra-and extra-axonal water diffusion to infer the axon diameter distribution (ADD) within a pack of nerve axons. The model assumes that within axons water diffusion is restricted by the surrounding axonal and myelinated membranes, whereas outside the axons, water diffusion is relatively free or hindered. By varying both the diffusion time and the diffusion weighting, one can estimate the ADD that represents the best fit of the analytical model to the experimental magnetic resonance data (Assaf etal.,2008. MagnResonMed; 59:1347–54).
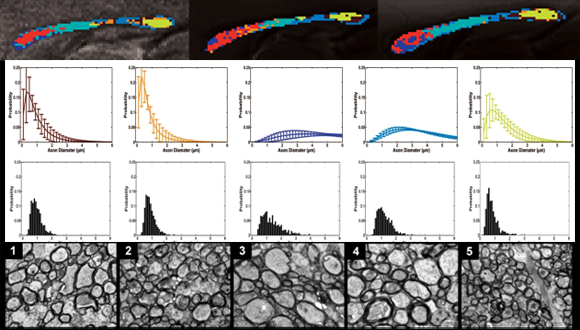
Barazany D et.al (2009)
Publication from our center:
Barazany D, Basser PJ, Assaf Y. 2009. In vivo measurement of axon diameter distribution in the corpus callosum of rat brain. Brain 132:1210-20.
Angular double-pulsed-field-gradient MRI (d-PFG)
Double pulsed-field gradient (d-PFG) MRI can provide quantitative maps of microstructural quantities and features within porous media and tissues not detectable by PFG MRI. Multiple-PFG MR sequences are constructed by concatenating two or more PFG MR Sequences. This enables one to observe or measure correlations between net displacements of spins during multiple diffusion periods, from which one can infer a number of fine-scale features. For instance, by varying the mixing time sm – the time between the PFG blocks—different microstructural parameters can be extracted (Komlosh et al. 2011, Journal of Magnetic Resonance 208 128–135).
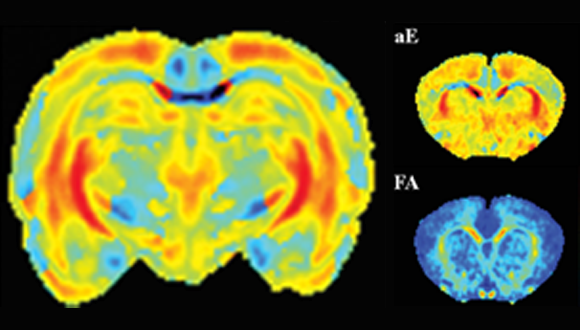
Shemesh N et.al (2012)
Publication from our center:
Shemesh N, Barazany D, Sadan O, Bar L, Zur Y, et al. (Cohen Y) 2012. Mapping apparent eccentricity and residual ensemble anisotropy in the gray matter using angular double-pulsed-field-gradient MRI. Magn Reson Med 68(3):794-806
Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST)
CEST imaging is a relatively new MRI contrast approach in which exogenous or endogenous compounds containing either exchangeable protons or exchangeable molecules are selectively saturated and, after transfer of this saturation, detected indirectly through the water signal with enhanced sensitivity. CEST- MRI method takes advantage of magnetization transfer between residues with exchangeable protons, such as amine, amide or Hydroxyl and water, enabling their detection at low concentrations. The enhanced sensitivity of the method enables obtaining images of endogenous cellular components or exogenous agents by MRI. The imaging of glucose, 2DG and FDG using CEST MRI was recently demonstrated and suggested to be useful for cancer diagnosis.
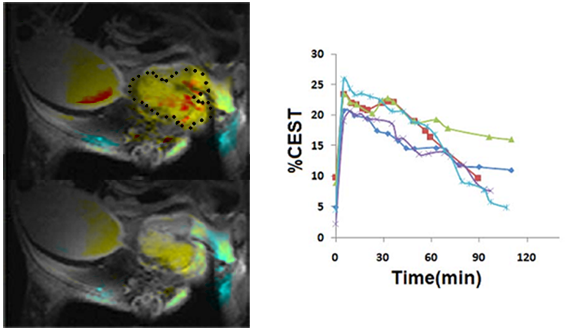
Rivlin M et.al (2014)
Publication from our center:
Rivlin M, Tsarfaty I, Navon G. 2014. Functional molecular imaging of tumors by chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI of 3-O-Methyl-D-glucose. Magn Reson Med. 72(5):1375-80.
Rivlin M, Horev J, Tsarfaty I, Navon G. 2013. Molecular imaging of tumors and metastases using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI.Sci Rep. 25;3:3045
Magnetization EXchange Imaging (MEXI)
A new MRI method that gives a new type of contrast based on magnetization exchange rates between water and macromolecules.
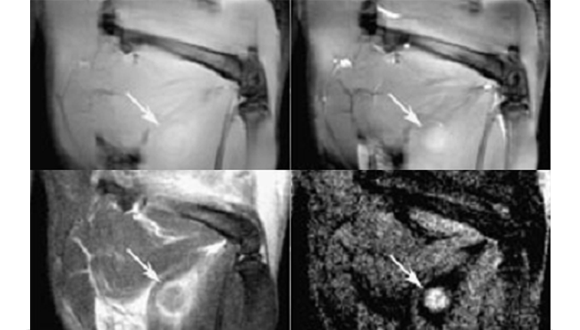
Carasso D et.al (2008)
Publication from our center:
Carasso D, Hanannel A, Navon G. 2008. A new MRI method, tested in vitro for the assessment of thermal coagulation and demonstrated in vivo on focused ultrasound ablation. NMR Biomed 21:637-43.